Which Os Service Provides Functions That Are Helpful To The User
What is an operating organisation?
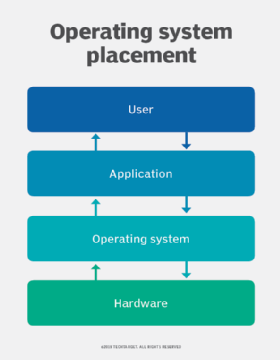
An operating organisation (OS) is the program that, afterwards being initially loaded into the computer past a boot program, manages all of the other application programs in a estimator. The application programs make employ of the operating system by making requests for services through a defined application program interface (API). In addition, users can collaborate directly with the operating system through a user interface, such as a command-line interface (CLI) or a graphical UI (GUI).
Why use an operating arrangement?
An operating system brings powerful benefits to computer software and software development. Without an operating organisation, every application would need to include its ain UI, besides as the comprehensive code needed to handle all low-level functionality of the underlying computer, such as disk storage, network interfaces and then on. Considering the vast array of underlying hardware available, this would vastly bloat the size of every awarding and brand software evolution impractical.
Instead, many common tasks, such as sending a network packet or displaying text on a standard output device, such as a display, tin be offloaded to system software that serves equally an intermediary between the applications and the hardware. The system software provides a consistent and repeatable way for applications to interact with the hardware without the applications needing to know any details about the hardware.
Equally long equally each application accesses the same resources and services in the same way, that system software -- the operating organisation -- can service almost any number of applications. This vastly reduces the amount of time and coding required to develop and debug an application, while ensuring that users can control, configure and manage the system hardware through a mutual and well-understood interface.
One time installed, the operating system relies on a vast library of device drivers to tailor OS services to the specific hardware surroundings. Thus, every application may make a common phone call to a storage device, merely the Bone receives that call and uses the corresponding driver to translate the call into actions (commands) needed for the underlying hardware on that specific reckoner. Today, the operating organization provides a comprehensive platform that identifies, configures and manages a range of hardware, including processors; memory devices and memory direction; chipsets; storage; networking; port advice, such as Video Graphics Array (VGA), Loftier-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) and Universal Series Omnibus (USB); and subsystem interfaces, such as Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe).
Functions of an operating system
An operating organization provides 3 essential capabilities: It offers a UI through a CLI or GUI; it launches and manages the awarding execution; and it identifies and exposes system hardware resources to those applications -- typically, through a standardized API.
UI. Every operating organisation requires a UI, enabling users and administrators to interact with the Bone in order to set, configure and even troubleshoot the operating system and its underlying hardware. In that location are two primary types of UI available: CLI and GUI.
The CLI, or terminal mode window, provides a text-based interface where users rely on the traditional keyboard to enter specific commands, parameters and arguments related to specific tasks. The GUI, or desktop, provides a visual interface based on icons and symbols where users rely on gestures delivered by human interface devices, such as touchpads, touchscreens and mouse devices.
The GUI is most ofttimes used by coincidental or end users that are primarily interested in manipulating files and applications, such as double-clicking a file icon to open the file in its default application. The CLI remains popular amid advanced users and system administrators that must handle a serial of highly granular and repetitive commands on a regular basis, such every bit creating and running scripts to prepare new personal computers (PCs) for employees.
Awarding management. An operating system handles the launch and management of every application. This typically supports an array of behaviors, including timesharing multiple processes, or threads, and so that various tasks tin can share the available processors' fourth dimension; handling interruptions that applications produce to gain a processor's immediate attention, ensuring there is enough retention to execute the application and its respective data without interfering with other processes; carrying out fault treatment that can gracefully remove an application's processes; and performing memory management without disrupting other applications or the Os.
An operating organization can as well support APIs that enable applications to utilize OS and hardware functions without the need to know anything about the depression-level OS or hardware state. Every bit an instance, a Windows API can enable a program to obtain input from a keyboard or mouse; create GUI elements, such as dialog windows and buttons; read and write files to a storage device; and more. Applications are near always tailored to use the operating system on which the awarding intends to run.
Additionally, an operating system can perform the post-obit services for applications:
- In a multitasking operating organisation, where multiple programs tin be running at the same time, the Os determines which applications should run in what order and how much time should be allowed for each application before giving another awarding a turn.
- It handles input/output (I/O) to and from attached hardware devices, such as hard disks, printers and dial-up ports.
- Information technology sends messages to each application or interactive user -- or to a organization operator -- about the status of operation and any errors that may have occurred.
- It can offload the direction of batch jobs -- for example, printing -- so that the initiating application is freed from this piece of work.
- On computers that can provide parallel processing, an operating system can manage how to divide the program so that it runs on more than ane processor at a fourth dimension.
All major calculator platforms (hardware and software) crave, and sometimes include, an operating organisation, and operating systems must exist developed with different features to meet the specific needs of diverse class factors.
Device management. An operating system is responsible for identifying, configuring, and providing applications with common admission to underlying computer hardware devices. Every bit the OS recognizes and identifies hardware, the OS volition install corresponding device drivers that enable the Os and applications running on the OS to utilise the devices without any specific knowledge of the hardware or devices.
An operating arrangement is responsible for identifying the correct printer and installing the appropriate printer drivers then that an application needs to merely brand calls to the printer without having to apply codes or commands that are specific to that printer -- that is the operating system's job. The state of affairs is similar for other devices, such equally USB ports; networking ports; graphics devices, such as graphics processing units (GPUs); motherboard chipsets; and storage devices, such as Serial-Attached SCSI (SAS) deejay adapters and disks that are formatted with a suitable file arrangement.
The OS identifies and configures concrete and logical devices for service and typically records them in a standardized structure, such as Windows Registry. Device manufacturers periodically patch and update drivers, and the Bone should update them to ensure best device performance and security. When devices are replaced, the Os too installs and configures new drivers.
Operating arrangement types and examples
Although the fundamental roles of an operating system are ubiquitous, there are countless operating systems that serve a wide range of hardware and user needs.
General-purpose operating system. A general-purpose OS represents an array of operating systems intended to run a multitude of applications on a broad option of hardware, enabling a user to run one or more applications or tasks simultaneously. A general-purpose OS tin exist installed on many different desktop and laptop models and run applications from accounting systems to databases to web browsers to games. General-purpose operating systems typically focus on procedure (thread) and hardware management to ensure that applications can reliably share the wide range of calculating hardware nowadays.
Common desktop operating systems include the post-obit:
- Windows is Microsoft's flagship operating organisation, the de facto standard for home and concern computers. Introduced in 1985, the GUI-based Os has been released in many versions since then. The convenient Windows 95 was largely responsible for the rapid development of personal computing.
- Mac OS is the operating organization for Apple'southward Macintosh line of PCs and workstations.
- Unix is a multiuser operating system designed for flexibility and adjustability. Originally developed in the 1970s, Unix was one of the kickoff operating systems to exist written in the C language.
- Linux is a Unix-like operating system that was designed to provide PC users a gratis or low-cost alternative. Linux has a reputation equally an efficient and fast-performing system.
Mobile operating system. Mobile operating systems are designed to suit the unique needs of mobile computing and communication-axial devices, such as smartphones and tablets. Mobile devices typically offer limited computing resources compared to traditional PCs, and the OS must be scaled back in size and complication in order to minimize its own resource use, while ensuring acceptable resources for 1 or more applications running on the device. Mobile operating systems tend to emphasize efficient performance, user responsiveness and close attention to data treatment tasks, such as supporting media streaming. Apple iOS and Google Android are examples of mobile operating systems.
Embedded operating system. Not all calculating devices are general purpose. A huge assortment of dedicated devices -- including abode digital assistants, automated teller machines (ATMs), airplane systems, retail point of auction (POS) terminals and internet of things (IoT) devices -- includes computers that require an operating system. The principal difference is that the associated calculating device simply does one major thing, and so the OS is highly stripped down and defended to both performance and resilience. The OS should run speedily, non crash, and handle all errors gracefully in gild to continue operating in all circumstances. In most cases, the OS is provided on a chip that is incorporated into the actual device. A medical device used in a patient'due south life back up equipment, for instance, will employ an embedded OS that must run reliably in guild to proceed the patient alive. Embedded Linux is one example of an embedded OS.
Network operating system. A network operating system (NOS) is another specialized OS intended to facilitate communication between devices operating on a local expanse network (LAN). A NOS provides the advice stack needed to understand network protocols in gild to create, exchange and decompose network packets. Today, the concept of a specialized NOS is largely obsolete because other OS types largely handle network advice. Windows 10 and Windows Server 2019, for example, include comprehensive networking capabilities. The concept of a NOS is nonetheless used for some networking devices, such every bit routers, switches and firewalls, and manufacturers may employ proprietary NOSes, including Cisco Internetwork Operating Arrangement (IOS), RouterOS and ZyNOS.
Real-time operating system. When a computing device must interact with the real world within constant and repeatable time constraints, the device manufacturer may opt to use a real-time operating system (RTOS). For example, an industrial control organisation may direct the operations of a sprawling factory or power plant. Such a facility will produce signals from myriad sensors and also send signals to operate valves, actuators, motors and countless other devices. In these situations, the industrial control system must answer apace and predictably to changing real-globe weather condition -- otherwise, disaster may result. An RTOS must function without buffering, processing latencies and other delays, which are perfectly acceptable in other types of operating systems. Two examples of RTOSes include FreeRTOS and VxWorks.
The differences between operating system types are not absolute, and some operating systems tin share characteristics of others. For case, general-purpose operating systems routinely include the networking capabilities found in a traditional NOS. Similarly, an embedded operating system usually includes attributes of an RTOS, while a mobile operating system can still typically run numerous apps simultaneously like other general-purpose operating systems.
This was last updated in June 2021
Keep Reading About operating organisation (Bone)
- Compare the top mobile operating systems for developers
- What is the preferred developer operating system?
- Learn the main Linux OS components
- Compare Windows 10 Bone editions to determine the all-time fit
- Is macOS Catalina stable plenty for enterprise utilize?
Which Os Service Provides Functions That Are Helpful To The User,
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/definition/operating-system-OS
Posted by: graygoodir80.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Os Service Provides Functions That Are Helpful To The User"
Post a Comment